Laboratory of Cardiovascular Genomics
Dimitris Kardassis, PhD
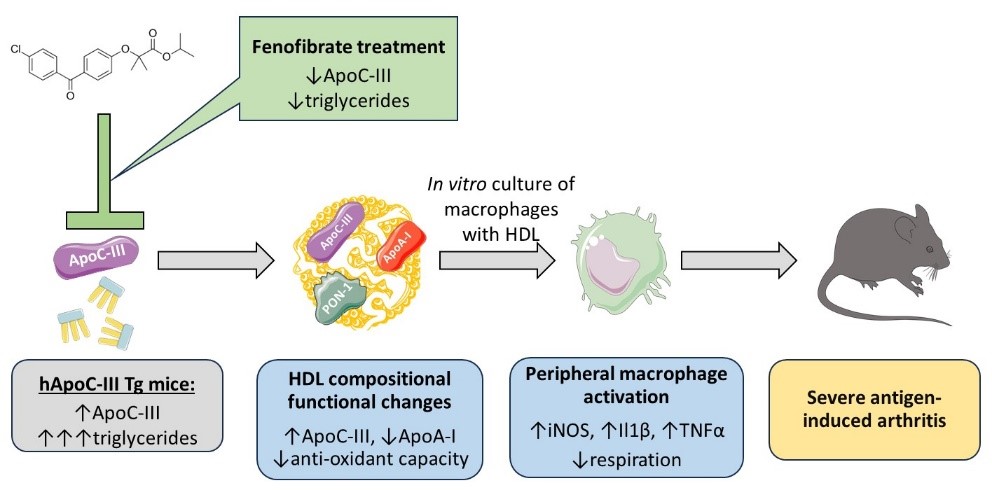
We are interested in understanding the molecular mechanisms by which High Density Lipoproteins (HDL) protect from atherosclerosis and how this atheroprotection is compromised by mutations in HDL genes or in chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. We also study the immunometabolism of atherosclerosis and how dyslipidemia affects the function of immune cells. We recently investigated the role of hypertriglyceridemia in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using a transgenic mouse model overexpressing the human ApoC-III gene. Using a protocol of antigen-induced RA, we showed that ApoC-III Tg mice exhibited significantly greater joint swelling, inflammatory infiltration and cartilage destruction compared to non-transgenic controls. These changes were accompanied by altered lipoprotein distribution in serum and HDL dysfunction. Treatment of arthritic mice with fenofibrate, a triglyceride-lowering drug, significantly ameliorated arthritis severity, restored HDL function and reduced macrophage activation. These findings highlight a mechanistic link between dyslipidemia, HDL dysfunction, and inflammatory exacerbation in RA and suggest that targeting ApoC-III-associated pathways may offer clinical benefit in patients with metabolic/inflammatory disorders (Axiotis I et al (2025). Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2025 Dec;1870(8):159686).
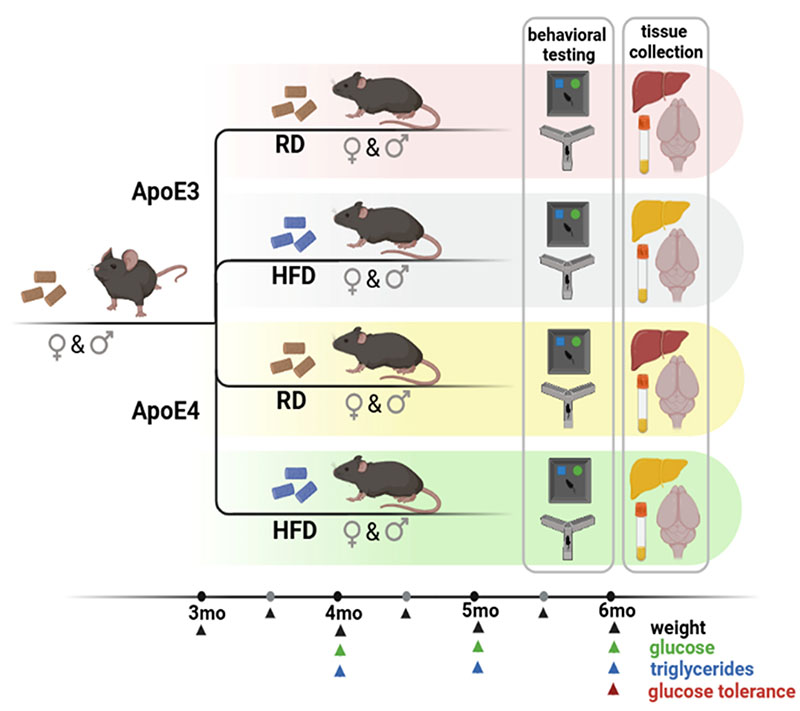
In a recent project funded by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (Elucidating the impact of Aapolipoprotein E and metabolic comorbidities on the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease https://apoemetabrain.gr/), our group studies the potential synergism between metabolic comorbidities such as dyslipidemia and brain ApoE4 in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). The ApoΕ4 isoform of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is the strongest risk factor for late-onset AD and it has been shown that dyslipidemia, type II diabetes and liver disease result in increased risk for AD and affect AD severity by unknown mechanisms. To achieve our goal we are using targeted replacement mouse lines expressing human ApoE3 or ApoE4 in combination with a high fat diet to induce hypercholesterolemia as well as double Tg mice expressing human ApoE along with human ApoC-III to induce hypertriglyceridemia. For the behavioral studies we are collaborating with the group of Prof. Kiki Sidiropoulou at the Department of Biology of UoC and affiliated member of IMBB-FORTH (Neurosciences group). Additionally, we are examining novel, non-canonical, roles of nuclear ApoE in AD pathogenesis in microglia using omics (ChIP-seq and proteomics). We expect that the proposed studies will provide new knowledge on how ApoE and metabolic comorbidities are involved on AD pathogenesis and may guide the design of novel therapeutic approaches for AD.
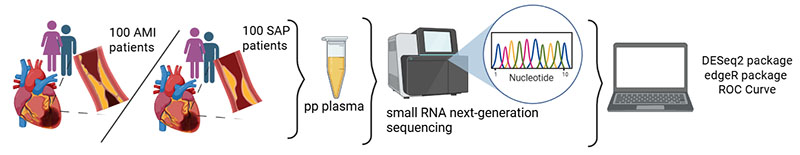
A third direction of our group is to identify though transcriptomics approaches circulating non-coding RNAs in patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes that could be utilized as biomarkers. For this purpose we are collaborating with European academic groups in Italy, Serbia, Spain, Romania and UK as well as with non-academic partners in a EU Horizon MCSA-SE project CasrdioSCOPE “Comprehensive and personalized assessment of acute coronary syndrome by multiomic approach and artificial intelligence strategy” (https://cardio-scope.eu/). The objectives of CardioSCOPE are: a) To discover novel pathological players for ACS and MACE by applying systems biology approach and multiomics analysis, b) To develop multimarker models for better diagnosis of ACS and prognosis of MACE by applying data integration through machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) approaches, c) To validate developed multimarker models on independent cohorts, and d) To develop standard operative procedures (SOP) for measuring and evaluating ACS markers using wet lab and dry lab working protocols.
Our projects are funded by: a) The Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (HFRI) Research Program “Funding Projects in Leading-Edge Sectors – RRFQ: Basic Research Financing (Horizontal support for all Sciences) grant No 15529 “APOE-META-BRAIN”, b) MSCA Staff Exchanges program CardioSCOPE Grant No 101086397, c) The Operational Programme “Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation” (NSRF 2014-2020) co-financed by Greece and the European Union Action “RESEARCH - CREATE – INNOVATE.




